BIOTECHNOLOGY aka BIOTECH
Another explanation
What is Biotechnology ?
At its simplest, biotechnology is technology based on biology - biotechnology harnesses cellular and biomolecular processes to develop technologies and products that help improve our lives and the health of our planet. We have used the biological processes of microorganisms for more than 6,000 years to make useful food products, such as bread and cheese, and to preserve dairy products..
And another one
What is Biotechnology ?
Well, biotechnology is the use of living organisms to make some kind of product. In the broader sense it is any technological application that involves usage of living systems. Let me give you some examples for better understanding. One such example is the usage of yeast to make beer, wine or bread. Or the usage of microorganism with the aim to create antibiotics.
Biotechnology
One of the oldest branches of science
Even though biotechnology as branch of applied life sciences is relatively new, it is also one of the oldest branches of science. Ancient Egyptians or Babylonians did brew beer circa 6000 B.C.
Biotechnology
The term Biotechnology was introduced by a Hungarian engineer, Karl Ereky in 1917. Ereky defined biotechnology as “ all lines of work by which products are produced from raw materials with the aid of living things”.
What are the biotech sectors ?
The Biotech industry is Huge
When we speak about the “biotechnology industry” it is in broad reference to a diverse group of treatments, biologics, diagnostics, medical devices, clinical laboratory tests, instruments, agricultural, industrial and biofuel applications. There are 10 divisions and colors are used for identification.
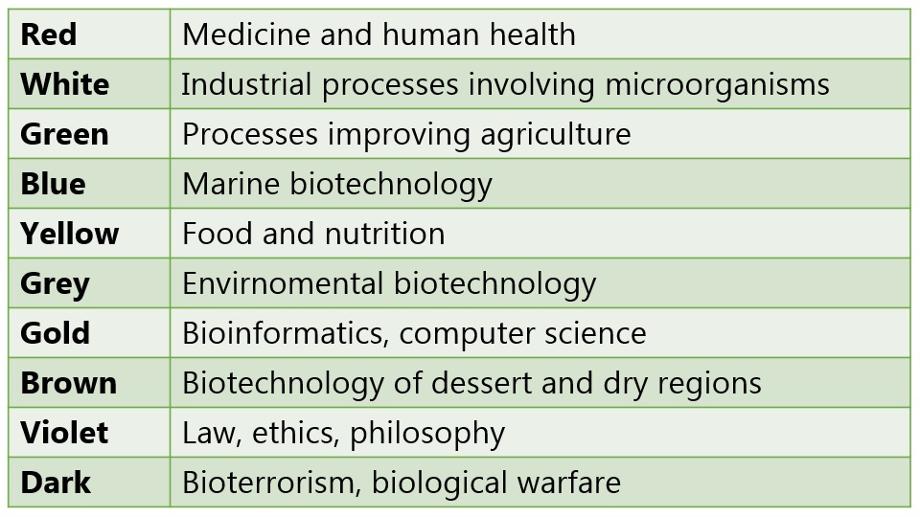
Biotech Sectors
What is the Red Biotech ?
This branch of biotech is also known as medical biotech or bio-pharmaceutical and it focuses on the production of medicines, vaccines, and drugs to help prevent and/or cure diseases. This branch has become a large factor in clinical research and gene therapy. Current clinical trials are using viruses to deliver genes for gene therapy against diseases such as congenital blindness and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
What is White Biotech ?
White biotechnology, also known as industrial biotechnology, involves employment of microorganisms in chemical production. An example is the already mentioned budding yeast in production of wine, bread or beer. But white biotechnology also encompasses production of biodegradable polymers, production of industrially relevant enzymes and microorganisms and production of fuel made from renewable sources. In addition, white biotechnology also aims in designing processes and products that consume little resources and energy compared to older, more traditional methods. It is considered as the biggest branch of biotechnology.
What is Green Biotech ?
Green biotechnology focuses on technologies that have positive impact on agriculture. This includes creation of new crops using genetic or traditional approaches as well as creation of new biofertilizers or biopesticides. This branch of biotechnology gives hope that one day food will be a commodity everyone can have. So called “golden rice“, containing genes of daffodil for the production of β-carotene – precursor of vitamin A, is a good example here. Over 230 millions people in Asian population suffer night blindness due to deficiency of vitamin A. Golden rice could help fight this problem and increase the quality of their lives.
What is Blue Biotech ?
Blue biotechnology focuses on marine organisms. Basically, it involves use of marine organisms or their products for creation of new medicaments, cosmetic products, food or food supplements. Considering that the sea presents the greatest biodiversity, there is potentially a huge range of sectors to benefit from the use of this kind of biotechnology.
What is Yellow Biotech ?
This is where we focus on food biotechnology and nutrition science. The overall goal of yellow biotech is to make food “better” and to grow food more sustainably. A popular example within this color, utilizing the power of fermentation, is the art of brewing beer.
What is Gray Biotech ?
Grey biotechnology tries to use living organisms to improve the environment we live in. This includes bioremediation that uses microorganism or even plants to clean up the environment from certain pollutants. It also tries to maintain biodiversity.
What is Gold Biotech ?
Gold biotechnology deals in bioinformatics, computers science, chip technology as well as nanobiotechnology. This includes search for primers, sequencing of peptides, search for alternations in DNA.
What is Brown Biotech ?
Brown biotechnology centres around treatment of desert-like soils drawing from species that are highly resistant to dry and saline soils. This involves mainly places such as Africa. In this case the use of GMO technology could make a beneficial impact using improved seeds to grow high-value commercial crops in low-rainfall areas. So yeah, basically, something dry resistant with sufficient crop yield. This branch is quite closely related to grey and green biotechnology.
What is Violet Biotech ?
Violet biotechnology is quite special. It actually centres upon the study of the legal aspects that surround this science. Biotechnology is something quite controversial and also potentially very dangerous. Therefore, it gives rise to heated emotions in almost anyone. Thus, the need for regulation and formation of a platform for discussion was necessary. This also includes biosecurity and moral impact of certain technologies (gene therapy, animal testing, etc.).
What is Dark Biotech ?
Dark biotechnology is not really something that anyone from science community takes part in, well, at least not in the bad part. It includes production of biological warfare and bioterrorism. It investigates pathogenic, virulent and resistant microorganisms, to convert them into biological weapons or counteract their harmful effects.
How do we use biotech everyday ?
Biofuel is obtained by fermenting sugars extracted from plants to ethanol, using a similar process like the one used in beer and wine-making. Biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel are blended with petrol and biodiesel to meet the legislation on greenhouse gas emissions.
When the blended biofuels are used in road transportation, the fuel can reduce their carbon impact.
Vaccines are introduced into the body’s immune system to fight pathogens when they attack. It is achieved by introducing weakened versions of the disease into the bloodstream.
The weakened disease pathogens are extracted using biotechnological techniques like growing the antigenic proteins in genetically engineered crops.
Bioremediation has to do with utilizing biotechnical applications to develop an enzyme that goes beyond pretreating some industrial and food waste components to allow for efficient removal of sewage systems.
Biotechnology has offered various techniques for the creation of crops that naturally display anti-pest characteristics.
So, instead of dusting and spraying the plants with pesticides, the plants become naturally resistant to pests. An example is the bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis genes being transferred to crops.
Environmental engineers have discovered a clean and safe way to dispose of waste. They do this by introducing nutrients to stimulate the activity of bacteria in the soil at the waste site. The bacteria digest the waste, thereby turning it into harmless byproducts.
After consuming the waste, the bacteria either die or return to their normal population levels. There are situations where the byproducts of the bacteria are useful and can be used for other valuable purposes.
For over 20 years, the cheese we eat is created with a biotech enzyme, chymosin — the natural enzyme found in calves and used to curdle milk during cheese production.
Using biotechnology to produce the enzyme makes it abundant and purer while removing the need to use animals to make cheese. Approximately 60% of all hard cheese products are now made with a biotech enzyme.
One of the most basic uses of biotechnology is in the area of alcohol production. Every day, people across the world would drink a glass or two. Beer, for example, is made from water, barley, brewer’s yeast, and flavouring.
During production, the starch contained in the barley is converted to sugar by enzymes then fermented. Then, the brewer’s yeast metabolises the sugars to produce alcohol and carbon dioxide. The enzymes and microbes are standard tools used in industrial biotechnology.
Military weapons have gone biological. Therefore, military units and disaster responders are now faced with threats from biological and chemical substances.
There are now biotechnology-produced enzymes that can break down toxic chemicals, including nerve-damaging gases like Sarin and Somain.
Those dangerous gases are broken down in an effective, convenient, and environmentally-friendly way. The enzymes are simply mixed with water and sprayed at the site of the attack.
Every living organism has chromosomes which are made up of DNA sequence. The DNA sequence is unique for every individual.
Identifying the pattern of DNA sequences is done in forensic DNA analysis using biotechnological tools. DNA fingerprinting is a useful tool in identifying a suspect in a criminal investigation, in paternity cases or identifying unrecognizable victims in a catastrophe.
Biotech is used in every day life
Finally, you can see that biotechnology is used in every day life — from creating revolutionary products and technologies that fight against debilitating and rare diseases to reducing carbon emissions, promoting effective industrial manufacturing processes, creating pest-resistant crops, and ebeni in challenging areas such as forensic sciences and biodefence.
Source: https://www.aimst.edu.my/event-news/how-biotechnology-used-everyday-life/
Biotech vs. Pharma:
What's the Difference ?
Biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies both produce medicines, but the medicines made by biotechnology companies are derived from living organisms while those made by pharmaceutical companies generally have a chemical basis.
Why is Biotech important ?
Biotechnology has helped improve food quality, quantity and processing.
It also has applications in manufacturing, where simple cells and proteins can be manipulated to produce chemicals.

The Pros and Cons of Biotech
The Pros of Biotechnology
-
It can improve health and reduce hunger simultaneously.
-
It creates flexibility within the food chain.
-
It offers medical advancement opportunities.
-
It allows us to preserve resources.
-
It helps us minimize or eliminate waste products.
-
It can reduce infectious disease rates.
The Cons of Biotechnology
-
It creates an all-or-nothing approach.
-
It is a field of research with many unknowns.
-
It could ruin croplands.
-
It turns human life into a commodity.
-
It can be used for destruction.
Special Considerations
Biotechnology companies generally have very high operating costs as they are involved in research, development, and testing that takes years to complete. The result could be a historic breakthrough or utter failure. Investors in their stocks are along for the ride, up or down.
Also, this industry may find roadblocks to the development of new products if the research or end product is controversial. As an example, several countries ban genetically modified plants and products.
Biotech has been given one advantage to make up for its cost disadvantage. While pharmaceuticals generally hold exclusive rights to manufacture and distribute their drugs for five years, biotech can get patent protection for 12 years.
Wikipedia
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is a broad area of biology, involving the use of living systems and organisms to develop or make products. Depending on the tools and applications, it often overlaps with related scientific fields. In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, biotechnology has expanded to include new and diverse sciences, such as genomics, recombinant gene techniques, applied immunology, and development of pharmaceutical therapies and diagnostic tests. The term biotechnology was first used by Karl Ereky in 1919, meaning the production of products from raw materials with the aid of living organisms.
Biotechnology consulting
Biotechnology consulting (or biotech consulting) refers to the practice of assisting organizations involved in research and commercialization of biotechnology in improving their methods and efficiency of production, and approaches to R&D. This assistance is usually provided in the form of specialized technological advice and sharing of expertise. Both start-up and established organizations would hire biotechnology consultants mainly to receive an independent and professional advice from key opinion leaders, individuals with extensive knowledge and experience in a particular area of biotechnology or biological sciences, and, often, to outsource their projects for implementation by well qualified individuals. Large management consulting firms would often be able to provide technological advice as well, depending on the qualifications of their consulting team. With the growth of pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology consulting has recently developed into an industry of its own and separated from the management consulting industry that traditionally also provides technological advice on R&D projects to various industries. This has also been fueled by the impact various conflicts of interests can have on commercialization when biotechnology organizations contract services from academic institutions or government scientists
This is exemplified by the successful emergence of many consulting companies dedicated exclusively to servicing the biotech industry. Occasionally, university professors and Phd students engage in biotechnology consulting, either commercially or free of charge.[citation needed]
A special type of consulting is patent strategy and management consulting or simply patent consulting which specifically emphasizes on the scope of patent rights versus R&D in industry. It also assets successful commercialization of patentable matter. The primary aim of patent consulting company is to assist various small, medium and large corporation in realizing their research project toward successful patent registration with minimized danger of infringement and other risks that patent registrations may be subjected to prior to commercialization. One example of patent consulting firm is The Patent World.
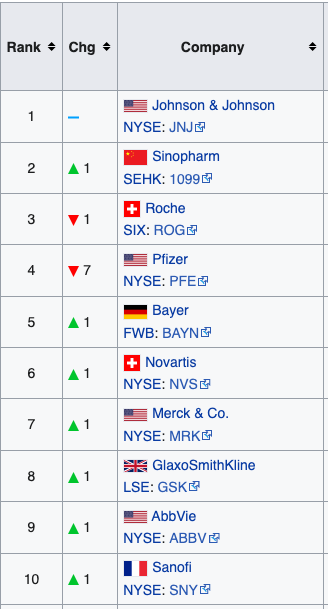
List of largest biomedical companies by revenue